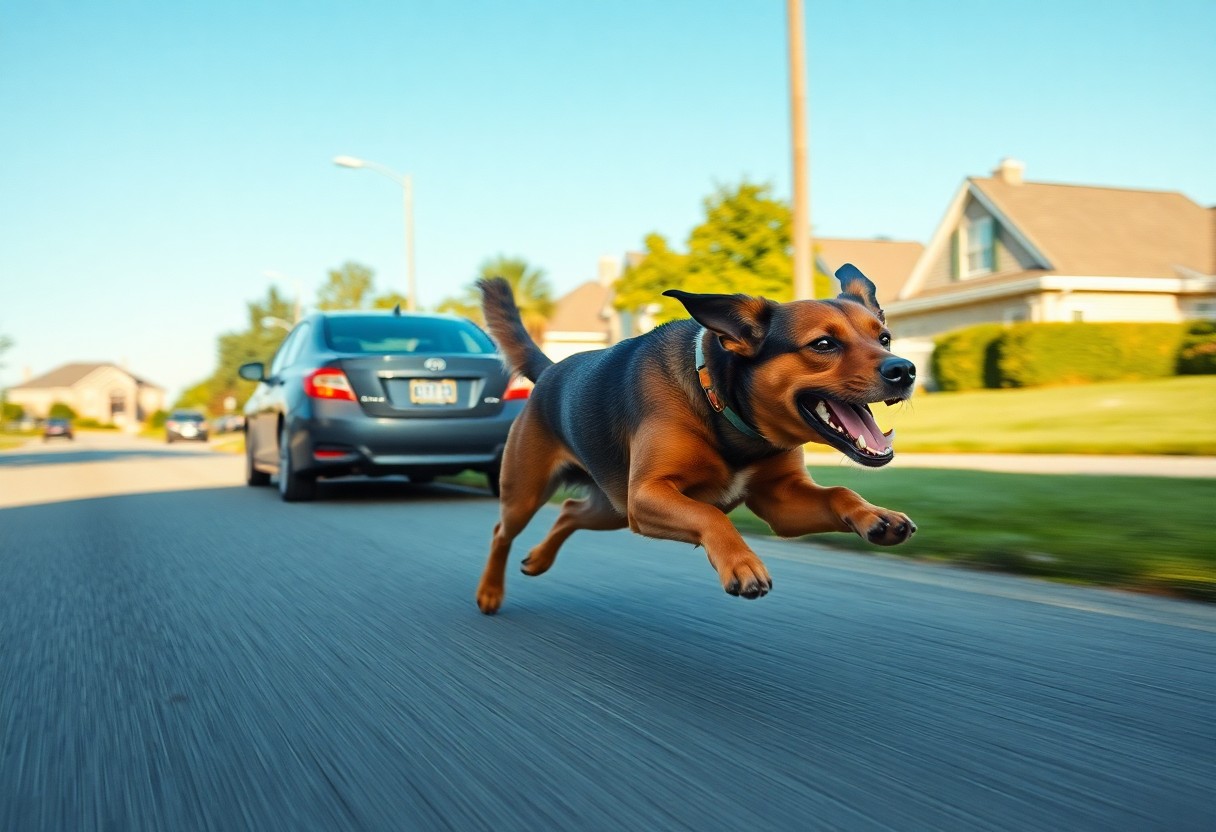
Behaviorally, you might have noticed your dog chasing cars or bikes and wondered why this happens. This instinct is often linked to a dog’s natural predatory drive and territorial instincts, compelling them to pursue moving objects. While this reaction can be seen as a playful or protective behavior, it can also pose significant dangers to your dog’s safety and others on the road. Understanding these instincts helps you manage and redirect your dog’s behavior effectively, ensuring both enjoyable walks and safer environments.
Understanding Canine Instincts
The instincts driving your dog to chase cars or bikes are deeply ingrained behaviors shaped by genetics and evolution. These instincts manifest as a natural reaction to movement and speed, triggering a chase response that can be both entertaining and concerning. Understanding these behaviors helps you manage and respond to your dog’s impulses effectively.
Predatory Behavior
To comprehend why your dog chases moving objects, you need to recognize the role of predatory behavior, an ancient survival mechanism. Your dog’s chase is a manifestation of their instinct to pursue fleeing prey, which activates their attention and excitement. This natural response can sometimes lead to dangerous situations if left unmanaged.
Herding Instincts
For dogs with herding backgrounds, chasing moving cars or bikes often stems from their instinct to control and guide moving groups. This behavior reflects your dog’s drive to herd, triggered by the swift, erratic movement of vehicles. While this instinct can be useful for certain breeds, it may be risky around traffic.
A herding dog’s chase behavior is not aggression but an expression of a desire to organize and protect. Your dog may try to nip at wheels or circle around vehicles, which can pose danger to both dog and driver. However, with proper training, you can channel this instinct into safe activities like agility or obedience exercises, turning a potentially harmful behavior into a positive outlet for your dog’s natural energies.
1. Dogs chase due to instinctual prey drive activation.
2. Movement triggers their natural hunting behavior.
3. Chasing provides mental and physical stimulation.
4. Lack of training reinforces pursuit behavior.
5. Sudden motion excites their fight-or-flight response.
6. Proper exercise reduces urge to chase vehicles.

The Role of Breeds
While many dogs have the instinct to chase, breed characteristics significantly influence this behavior. Some breeds were historically bred for hunting or herding, making them more likely to react to moving objects like cars or bikes. By understanding how your dog’s breed traits affect their tendency to chase, you can better manage and train them to reduce this behavior. Your dog’s natural instincts are rooted deeply in their breed’s history and purpose.
Breeds Prone to Chasing
Before you decide how to train or handle chasing behaviors, it’s helpful to know which breeds are more prone to chase. For example, herding breeds like Border Collies and Australian Shepherds often have a strong desire to pursue moving targets. Similarly, hunting breeds such as Greyhounds or Coonhounds exhibit intense chasing instincts. If your dog belongs to one of these groups, their breed-specific urges may challenge your training efforts.
Genetic Factors in Behavior
To understand why your dog chases cars or bikes, you should consider the genetic factors influencing their behavior. Genetics play a role in your dog’s prey drive, energy levels, and reactivity. Dogs bred for specific work require more physical activity and mental stimulation, which can trigger chasing behaviors if unmet. Knowing your dog’s genetic predispositions helps you tailor your approach in managing their tendencies effectively.
Factors affecting your dog’s genetic behavior include:
- Prey drive intensity: Determines how strongly they respond to moving objects.
- Energy levels: Higher energy breeds often exhibit more chasing.
- Temperament traits: Some genetics influence boldness or focus.
Knowing these can help you understand the root of your dog’s chasing impulses and develop a suitable management plan.
Environmental Influences
All dogs are influenced by their surroundings, which play a significant role in whether they chase cars or bikes. Your dog’s behavior can be shaped by various environmental factors, including their daily exposure to traffic, stimuli intensity, and the area they live in. Understanding these influences helps you manage and modify your dog’s tendencies effectively, offering a safer environment for both your pet and others on the road.
Socialization and Exposure
At an early age, your dog’s socialization and exposure to moving vehicles and bikes impact how they react to these objects later in life. Regular, positive encounters with cars and bikes help reduce fear and the urge to chase. If your dog is isolated from such experiences, they might view cars or bikes as threats or prey, increasing chasing behavior. Ensuring well-rounded exposure can lead to a calmer, more controlled response in busy environments.
Urban vs. Rural Settings
Between city streets and open countryside, your dog’s chasing behavior can vary greatly. Urban settings are filled with numerous distractions and fast-moving vehicles, which can either desensitize or overstimulate your dog. In contrast, rural areas often have fewer vehicles but more open space, encouraging natural chasing instincts. Recognizing these differences helps you tailor training and supervision strategies specific to your dog’s living environment.
Rural dogs often have more space to roam freely, which can enhance their instinct to chase moving objects like bikes or cars. Unlike urban dogs, they experience fewer loud noises but may have stronger prey drives due to less frequent controlled exposure. This freedom can lead to dangerous situations when a dog bolts after a vehicle without consideration of traffic risks. As a responsible owner, you must balance giving your dog space with establishing firm boundaries to ensure their safety and the safety of others on the road.
Psychological Factors
After observing your dog’s behavior, you may notice several psychological factors that drive the urge to chase cars or bikes. These include:
- Fear and anxiety responses triggered by fast-moving objects
- Excitement and playfulness that mimic predatory instincts
- Territorial instincts prompting dogs to protect their space
After understanding these elements, you can better address and manage your dog’s chasing behavior.
Fear and Anxiety Responses
With some dogs, the reaction to speeding vehicles stems from fear and anxiety. Your dog may perceive cars or bikes as threats, triggering a natural flight or fight response. This heightened arousal can cause them to chase as a defensive reaction, seeking to create distance or override the perceived danger. Understanding this can help you approach the behavior with empathy and appropriate training strategies.
Excitement and Playfulness
Between your dog’s bursts of energy and the sudden appearances of moving objects, chasing can often be an expression of excitement and playfulness. This natural impulse is linked to their predatory drive and desire to engage in interactive play, making cars and bikes appealing targets. This behavior is generally harmless but can become risky if not managed properly.
A more detailed look at excitement-driven chasing reveals that your dog is responding to stimulating movement patterns that trigger instinctive play behaviors. This is positive in promoting exercise and mental engagement, but it becomes dangerous near busy streets or highways. Training and redirecting this playfulness towards safe activities are necessary steps you can take to protect your dog while satisfying their energetic needs.
Training and Behavioral Modification
Once again, understanding why your dog chases cars or bikes is key to effectively modifying this behavior. Through consistent training and behavioral modification, you can redirect your dog’s instinctual chase responses. It requires patience and targeted exercises to help your dog learn safer, more appropriate ways to engage with moving objects in their environment, ultimately enhancing both their safety and your peace of mind.
Techniques to Curb Chasing
Behavioral techniques such as teaching your dog to focus on you, using commands like “leave it” or “come,” and employing controlled leash walks can significantly reduce chasing incidents. By creating alternative behaviors and rewarding compliance, you establish a clear boundary for when chasing is unacceptable. Incorporating regular exercise and mental stimulation also helps reduce the excess energy that might trigger chasing impulses.
Positive Reinforcement Strategies
On the premise that dogs respond best to encouragement, positive reinforcement uses treats, praise, or play to reward your dog when they avoid chasing. This method not only strengthens good behavior but also builds your dog’s trust and willingness to listen. Over time, your dog learns that ignoring cars or bikes brings enjoyable outcomes, which can transform their natural instincts.
But to effectively apply positive reinforcement strategies, you need to be timely and consistent with rewards, ensuring you catch your dog in the act of making the right choice. Using high-value treats or favorite toys can enhance motivation, especially in distracting environments. Pairing reinforcement with clear commands and gradual exposure to triggers will help your dog develop new, safer habits without fear or confusion, significantly improving their behavior around moving objects.
Safety Considerations
Unlike a simple game, when your dog chases cars or bikes, you face serious safety concerns. You need to understand that this behavior can lead to accidents not only harming your pet but also putting yourself and others at risk. Ensuring the safety of your dog requires awareness of these dangers and proactive measures to prevent such behavior. Taking control of the situation protects your dog and helps maintain a safe environment for everyone on the road or sidewalk.
Risks Involved in Chasing
Involved in chasing fast-moving vehicles, your dog risks severe injuries like broken bones, bruises, or worse. This unpredictable behavior can startle drivers, potentially causing accidents that affect more than just your pet. Additionally, your dog can become disoriented, leading to further dangers like getting lost or running into traffic. Understanding these hazards helps you take steps to mitigate the risks and keep your dog safe in all situations.
Importance of Responsible Pet Ownership
Against leaving this behavior unchecked, being a responsible pet owner means setting clear boundaries and providing proper training to discourage chasing. You hold the responsibility to protect your dog from harm and prevent it from becoming a hazard to others. This includes leash control, secure fencing, and consistent behavior correction to enhance safety for your pet and those around you.
Importance lies in your active role in managing and training your dog. By doing so, you reduce the likelihood of injuries and accidents and foster a safer environment. You must invest time in obedience training, socialization, and using safe play alternatives to satisfy your dog’s instincts without jeopardizing safety. Cultivating this control not only benefits your dog’s well-being but also reinforces your status as a caring and responsible owner.
To wrap up
From above, understanding the science behind why dogs chase cars or bikes sheds light on their natural instincts and behavior patterns. You can see how their prey drive, territorial instincts, and excitement trigger this reaction. By recognizing these factors, you are better equipped to manage and redirect your dog’s behavior effectively. For deeper insight and practical tips, consider exploring Why Do Dogs Chase Cars, and What Can You Do About It? to enhance your approach to this common issue.
 wagwagtail "only love can make your dog wag her tail"
wagwagtail "only love can make your dog wag her tail"
