Just like you might fidget or explore your surroundings, your dog digs for a variety of reasons that are deeply rooted in its instincts and behavior. Understanding why your dog digs can help you address this natural habit effectively, whether it’s for play, hunting, or seeking comfort. However, digging can sometimes lead to damage in your yard or expose your pet to hazards like sharp objects or pests. By knowing the motivations behind this behavior, you can create a safe environment that satisfies your dog’s needs while protecting your property.
Natural Instincts
For your dog, digging is more than just a playful act; it taps into their natural instincts. This behavior is deeply rooted in their genetic makeup, inherited from wild ancestors who dug for shelter, food, and protection. Understanding these instincts helps you appreciate why sometimes your dog instinctively burrows into the earth, expressing behaviors that have supported survival over millennia.
Ancestral Behavior
The digging habit reflects behaviors passed down from your dog’s wild ancestors, such as wolves and wild canines. These animals dug to create dens for safety and warmth, and to hide food from other predators. By digging, your pet connects with these ingrained ancestral patterns, responding to inherited urges that are deeply embedded in their DNA.
Hunting and Foraging
Between hunting and foraging, digging serves as a method for your dog to uncover hidden prey or edible roots. This instinctive activity simulates natural hunting behaviors and satisfies their innate curiosity. It’s an outlet for energy and drive—key to your dog’s mental and physical well-being.
In addition to unearthing small animals or insects, digging allows your dog to engage in stimulating, purposeful activity. By encouraging this natural behavior in controlled ways, you can reduce destructive digging and channel their energy into positive outlets, helping maintain your dog’s happiness and health.
1. Dogs dig to explore instincts inherited from ancestors.
2. Digging helps dogs create cool resting spots.
3. Boredom or excess energy often triggers digging behavior.
4. Dogs dig to hunt or uncover hidden objects.
5. Anxiety or stress can lead to compulsive digging.
6. Providing toys and exercise reduces unwanted digging.
Environmental Factors
If you’re wondering why your dog digs in certain places, the environmental factors around them play a significant role. Consider these elements as triggers for digging behavior:
- Weather conditions such as heat or cold
- Soil type and texture
- Presence of insects or buried objects
- Nearby wildlife or scents
After observing these factors, you can better understand and manage your dog’s digging habits.
Temperature Regulation
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Reason | Dogs dig to create a cool, shaded spot to regulate body heat. |
| Common Behavior | Digging during hot weather to find cooler ground. |
| Purpose | Helps reduce overheating and discomfort. |
On hot days, your dog might dig more as a natural way to stay comfortable by cooling off under the surface soil.
Gardening and Landscape Interactions
Any gardener or landscape lover who owns a dog will notice that digging can affect the appearance and health of plants and soil. Dogs may disturb roots, uproot flowers, or damage mulch simply by trying to satisfy instincts tied to environmental stimuli.
Further, you should be aware that while digging can harm your garden and landscape, it also reflects important natural behaviors in your dog. By adjusting your landscaping choices or creating designated digging areas, you can channel this digging impulse safely and effectively, protecting your plants while respecting your dog’s instincts.
Emotional Triggers
Despite your dog’s varied reasons for digging, emotional triggers play a significant role. When your dog experiences feelings that are out of balance, such as anxiety or boredom, digging often becomes a coping mechanism. Understanding these emotional cues is vital to addressing the behavior effectively and soothing your dog’s inner needs.
Stress and Anxiety
Triggers like loud noises, unfamiliar environments, or separation from you can lead to stress and anxiety in your dog. Digging may serve as an outlet for these feelings, providing a sense of comfort or distraction. Recognizing this behavior as a sign of distress allows you to intervene and offer reassurance or additional support to your pet.
Boredom and Excess Energy
Boredom often prompts your dog to dig as a way to entertain themselves or burn off excess energy. Without adequate physical activity or mental stimulation, your dog may resort to digging to alleviate their restlessness and fill the void.
This behavior signals that your dog’s needs are not being fully met, and if left unchecked, it can lead to destructive habits or heightened frustration. Providing regular exercise, interactive toys, and engaging activities can help redirect this energy positively. Taking action not only protects your home but also fosters a healthier, happier bond between you and your pet.
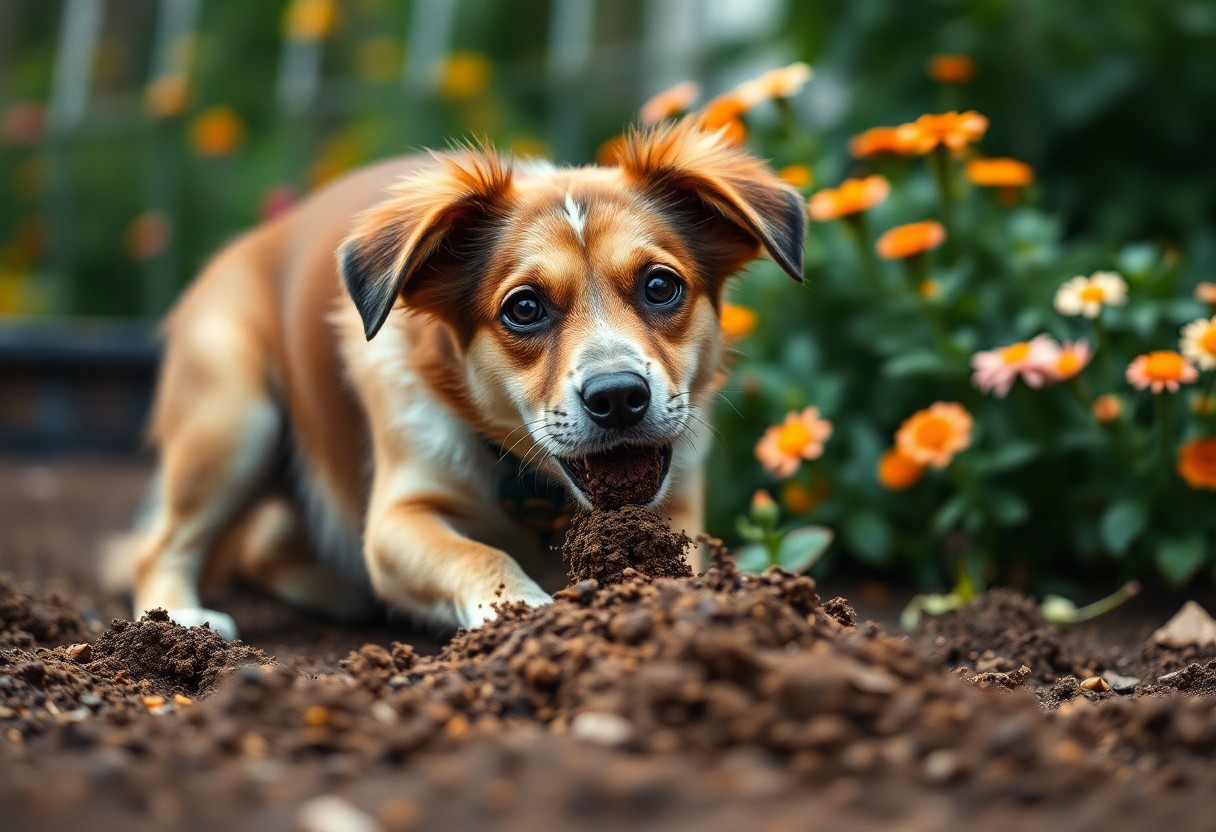

Communication Signals
To understand your dog’s digging behavior, you should consider it as a form of communication. Dogs use digging to express various needs and emotions. For deeper insight into this behavior, you may want to explore Reasons Why Dogs Like to Dig. Recognizing these communication signals can help you respond appropriately and improve your bond with your dog.
Marking Territory
At times, your dog digs to mark their territory. By disturbing the soil and leaving their scent, they assert ownership over a specific area. This behavior is an instinctual way for dogs to communicate boundaries and ensure other animals are aware of their presence.
Seeking Attention
On occasions, your dog might dig to get your attention. If your pet feels neglected or wants to engage with you, digging becomes a way to prompt interaction. This behavior often reflects their desire for companionship or playtime.
For instance, if you notice your dog digs persistently when you’re busy or distracted, this is a clear sign they seek your focus. Addressing this by setting aside quality time can reduce digging caused by attention-seeking. However, understand that ignoring repeated digging may lead to frustration or destructive habits, so responding thoughtfully is important for maintaining harmony between you and your pet.
Health-Related Issues
All dogs dig for various reasons, but some do so because of underlying health-related issues. If your dog is digging more than usual, it might be a sign that they are experiencing pain, discomfort, or irritation. Observing these behaviors closely can help you determine if there is a health concern that needs addressing. Ensuring your pet receives appropriate veterinary care can prevent these issues from worsening and improve their overall well-being.
Pain and Discomfort
Along with behavioral causes, digging can signal that your dog is dealing with pain or discomfort in specific areas. For example, conditions like arthritis or injuries can drive your dog to dig as a way to alleviate discomfort or divert their attention. You should watch for additional signs like limping or sensitivity to touch, which may indicate the need for a veterinary checkup and tailored treatment.
Parasites and Allergies
Beside pain, your dog’s digging might be linked to parasites or allergies. Fleas, ticks, or mites can irritate your dog’s skin, causing itching that encourages digging as an attempt to relieve the itch. Allergies can also trigger excessive scratching and digging, especially if your pet is allergic to pollen, food, or environmental factors. These symptoms often require medical intervention to manage effectively.
And if your dog has persistent parasites or allergies, the effects can be dangerous to their health, potentially leading to infections or severe skin damage. Paying attention to these signs and working with your vet to provide early treatment will help reduce discomfort and prevent complications. Your involvement in monitoring and responding promptly is crucial to maintaining your dog’s health and comfort.
Management Strategies
Many dog owners find digging to be a challenging behavior to manage. By understanding why your dog digs and applying consistent strategies, you can address this behavior effectively. Implementing appropriate management techniques helps protect your garden and property while also satisfying your dog’s natural instincts. While it may take time and patience, these strategies can lead to a happier, well-behaved dog and a peaceful living environment.
Redirecting Digging Behavior
Around your yard, you can engage your dog in more constructive digging activities. Providing a designated digging area filled with soft soil or sand encourages your dog to dig in a controlled space. You might enhance this area with toys or buried treats to make it more appealing. Redirecting your dog’s digging habit this way helps prevent damage to gardens and reduces frustration for both you and your pet.
Creating Safe Spaces
Management of your dog’s environment is key in minimizing unwanted digging. Creating safe spaces means establishing areas where your dog can dig without harm or destruction to your property. By designating these zones, you provide a healthy outlet for natural behaviors, ensuring both your dog’s well-being and the safety of your home grounds.
Redirecting your dog’s digging to safe, controlled areas not only keeps your garden intact but also satisfies their instinctive needs. You can enhance these spaces by adding familiar scents or toys, making them more attractive. Providing consistent encouragement and supervision in these areas encourages your dog to adopt these spaces as their preferred digging spots, ultimately resulting in positive reinforcement of good behavior and stronger bonds between you and your pet.
Final Words
With this in mind, understanding why dogs dig helps you address their natural instincts and needs more effectively. Whether they dig out of boredom, to seek comfort, or to explore, recognizing these behaviors allows you to provide better outlets and environments for your dog. By meeting their physical and mental stimulation requirements, you can reduce unwanted digging and strengthen your bond while ensuring your dog remains happy and healthy.
 wagwagtail "only love can make your dog wag her tail"
wagwagtail "only love can make your dog wag her tail"
